Boeing chip experts eye design breakthroughs in electronics thermal management
Officials of U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, awarded a $2.1 million contract to Boeing for the Intrachip/Interchip Enhanced Cooling Applications (ICECool Applications) program.
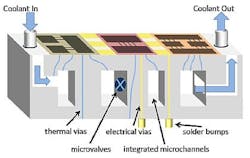
ICECool Applications is a major new initiative to demonstrate advanced electronics cooling techniques for high-performance embedded computing (HPEC) and RF monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC) power amplifiers with convective or evaporative microfluidic cooling built directly into the electronic devices and packaging.
The Air Force Research Lab awarded the ICECool Applications contract to Boeing on behalf of the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in Arlington, Va., which is sponsoring the program. Boeing's involvement in ICECool Applications will be a 30-month effort.
Boeing experts will try to enhance the performance of RF power amplifiers and embedded computing by removing one kilowatt per square centimeter heat flux, as well as one kilowatt per cubic centimeter heat density, in high-performance embedded computing boards and RF MMICs.
Boeing is the second U.S. defense company to take part in the DARPA ICECool program. Last April researchers at IBM Corp. in Armonk, N.Y., won a $5 million contract for the ICECool Fundamentals program to develop the fundamental building blocks of intra- and interchip evaporative microfluidic cooling.
Essentially, DARPA scientists want to make cooling just as important as any other aspect of chip design, and use embedded thermal management to enhance the performance of military electronics. Integrating chips with convective or evaporative microfluidic cooling, DARPA officials say, has the potential to speed the evolution of advanced chip integration.
One fundamental problem that electronic systems designers have today is the large size and weight of cooling subsystems. Ever-smaller chip geometries generate increasing amounts of heat, and the ability to cool electronics is moving more slowly than the ability to shrink chip densities.
This causes some advanced electronics to perform well below the inherent electrical limits of the device technology. Integrating cooling directly into the chip could transform electronic systems architectures and overcome the SWaP bottleneck in advanced electronics, DARPA officials say.
The ICECool program complements other DARPA thermal-management initiatives, such as the Thermal Ground Plane (TGP) program to develop modern high-performance heat spreaders to replace the copper alloy spreaders in conventional systems; the Microtechnologies for Air Cooled Exchangers (MACE) program to develop enhanced heatsinks that reduce the thermal resistance and power requirements for cooling fans; and the Active Cooling Module (ACM) program to develop miniature, active, high-efficiency refrigeration systems based on thermoelectric or vapor-compression technologies.
For the ICECool Applications, DARPA officials say they expect to award several contracts, so Boeing likely will not be the only company involved in this phase of the ICECool program.
For more information contact Boeing Defense, Space & Security online at www.boeing.com/boeing/bds, or DARPA at www.darpa.mil.